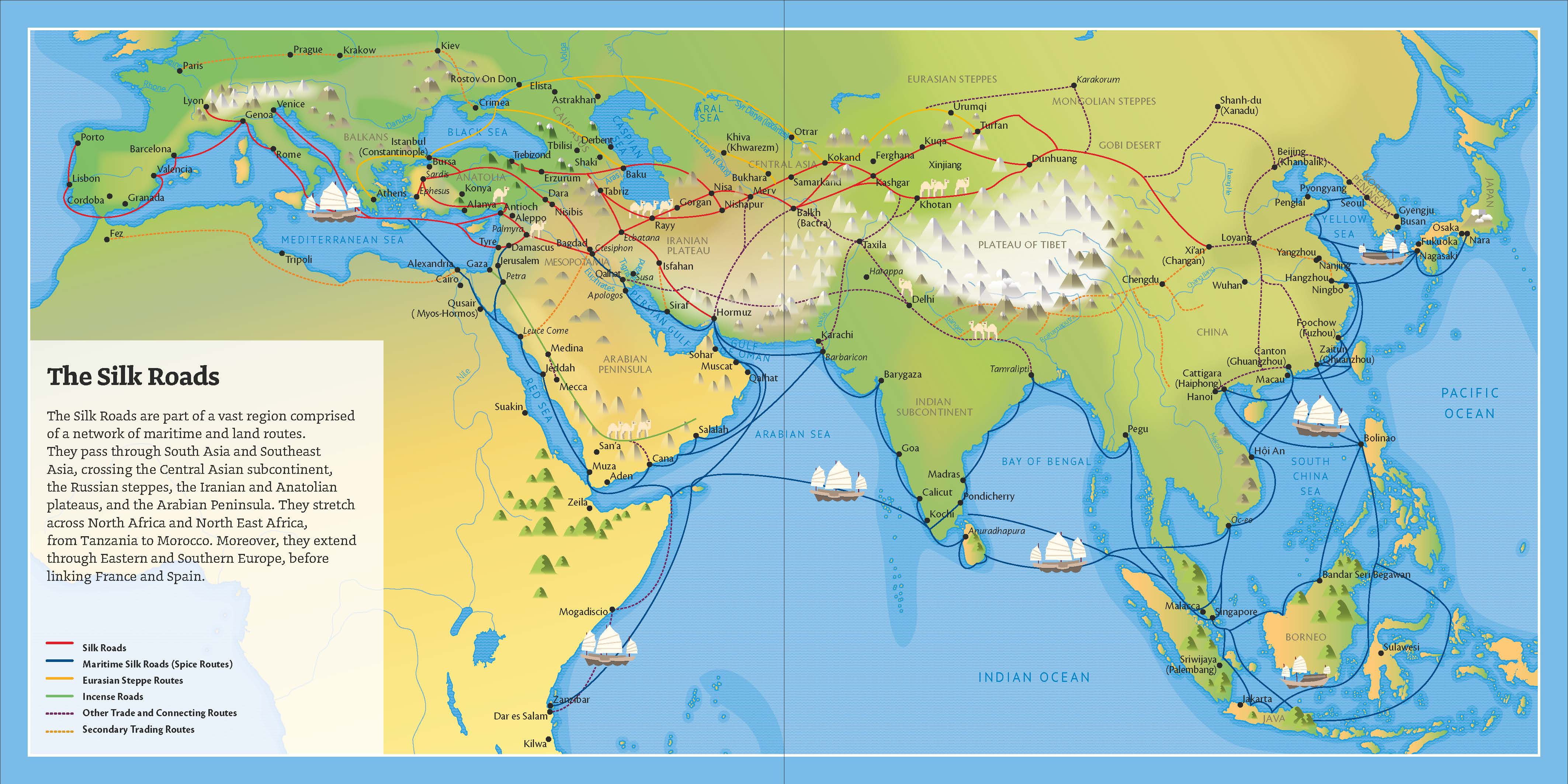
Anatolia, due to its geographic location, is functioned as a gate and bridge between west and east as well as being a place on where various civilizations are founded and developed since ancient ages. As a result of this, during various periods, road webs with various directions and character such as Kings Road (VIth century B.C., Roman Era Roads (IInd century B.C.), have surrounded the Anatolia. Transportation of silk and spice as well as other products of east to west, is formed commercial roads named as “Silk Road” today and reaching Europe from China.
But, Silk Roads were not only the commercial roads but also maintained cultural relations between east and west for centuries. Anatolia, is formed one of the most important junction points of Silk Road. During Medieval Age, silk roads have reached Europe over Thrace with passing Anatolia, which has a characteristic of being a bridge with following more than one routes in Middle Asia, beginning from China. Also, Europe is reached by maritime lines with using important harbors such as Efes and Milet, at Aegean coasts, Trabzon and Sinop, in Black Sea Alanya and Antalya in Mediterranean.
Silk Road in Anatolia,Turkey
At North
Trabzon, Gumushane, Erzurum, Sivas, Tokat, Amasya, Kastamonu, Adapazari, Izmit, Istanbul, Edirne;
At South
Mardin, Diyarbakir, Adiyaman, Malatya, Kahramanmaras, Kayseri, Nevsehir, Aksaray, Konya, Isparta, Antalya, Denizli centers are followed. It is known that Erzurum, Malatya, Kayseri, Ankara, Bilecik, Bursa, Iznik, Izmit, Istanbul route is also used. Extension of Antalya – Erzurum route, composed with connections of Sivas and Kayseri on North and South routes, is connecting Anatolia to Iran and Turkmenistan.
On this commercial axis, maritime lines besides road is also used, and it is following.
In Black Sea
Coming from North to Trabzon, Samsun, Sinop, Istanbul, Bursa, Gelibolu, Venedik over Batum;
In Mediterranean
Antakya, Antalya, Izmir (Foca), Europe line over Syria.
After 14th century, Silk Road continued its importance, and begin to loose its vigor as a result of inventions made during New Age. On 16th and 17th centuries, after begun of cultivation of silk in Europe, it has faced with the danger of loosing its former importance. Caravans become vanish and products of Far East begun to loose their attraction with increasing maritime activities. Silk Road become not used beginning from 19th century. Seljukians who supplied the secure dispatch of rich products of east to West over Anatolia during Medieval Age, had remained the commercial activities live and increase the wealth of the state with the measures taken by them. Because commerce in Medieval Age Anatolia was among the activities which are first degree effecting the wealth of the state.
Seljukians, had signed commercial agreements with foreigners; had given commercial independence to Christian merchants in Anatolian lands like Muslim merchants; and had maintained state security against robberies and all kinds of damages that they can face during their voyages. Seljukians were the first state that used “state insurance system” for securing the commercial life and also they had tried to promote commercial life with the deduction applied on custom dues. Inn and caravansaries, are organization who played important role in this active environment. These magnificent structures who have a great impact on architecture with their appearances remembering a castle on desolate roads, their rick rock adornments and improved place designs, are carefully considered in connection with application of a strong road policy and a certain transportation program.
In caravansaries constructed both during Seljukian and Ottoman periods, caravans were protected by military units. Lives and property of the voyagers were warranted during their stays in caravansaries, and there were foundations for covering the expenses incurred due to all kinds of maintenance and performance of services. These structures were the bases where reinforcement of army related with previously stocked ammunition and provisions during expedition is eased, and break points of merchants in which they had marketed their goods, besides the characteristics of voyages and commerce were under warranty and were maintaining the social solidarity.
They were generally constructed with distances of 30 – 40 kilometers, not exceeding 8 – 10 hours by foot and takes a day with camels. The ones constructed by statesmen or benefactors were known as “INN” and the bigger and magnificent ones constructed by Sultans were known as “SULTAN INN” among the accommodation organizations constructed by Anatolian Seljukians on these commercial roads. The reason for constructing rural areas established inns and caravansaries as structures similar to castles and closed to outside with their thick and dull walls at that age, was security. There were rooms for accommodation of voyagers, divisions for securing the goods and rest of their horses, small mosques, bath chambers, foundations as well as horseshoer, doctor, veterinary, cage and harness repair services within them.
The passengers accommodated within inn and caravansaries can stay for three days without paying regard to their religion, language and race, and they were cured if they were sick. No charge is taken from these passengers, who were given two meals Per day, whose bath needs were covered, whose animals were cared and fed for three days, and all expenses were covered by foundations. How to be managed these foundations in their founds, what were their incomes, working conditions of their staff and their wages were mentioned clearly. According to the results of the researches, it is determined that there were approximately 200 inns and caravansaries in Anatolia.